ABOUT
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, is a hereditary androgen-dependent hair loss condition that affects both men and women. It is the most common form of hair loss and is characterized by a gradual and predictable pattern of hair thinning and loss. This type of hair loss is primarily influenced by genetic and hormonal factors.
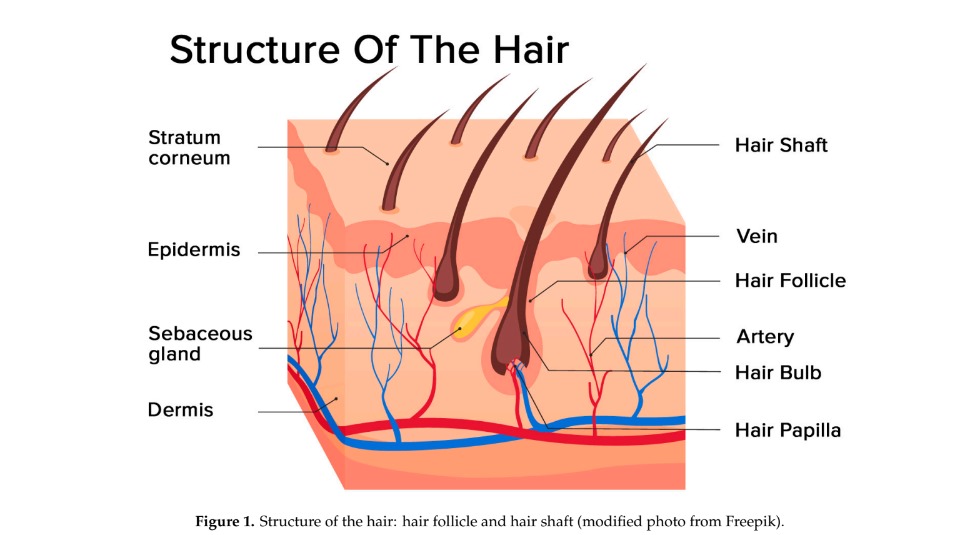
Here are some key points to understand about androgenic alopecia:-
Genetic Predisposition: -
The primary factor contributing to androgenic alopecia is genetic inheritance.
Hormonal Influence: -
Androgenetic alopecia is linked to androgens, which are male hormones present in both men and women. The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a crucial role in the development of this condition. DHT is derived from testosterone and is known to shrink hair follicles over time, leading to shorter and finer hair growth.
Pattern of Hair Loss:-
In men, androgenetic alopecia typically follows a distinctive pattern, starting with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. Women may experience a more diffuse thinning of hair across the scalp without a distinct pattern.
Age of Onset: -
The onset of androgenetic alopecia varies, but it often begins in adulthood.
Progression: -
Hair loss in androgenetic alopecia tends to be gradual. Over time, affected hair follicles produce finer and shorter strands, leading to an overall decrease in hair density. In severe cases, complete baldness may occur, especially in men.
Medical and Non-Medical Treatments:-
While there is no cure for androgenic alopecia, various treatments are available to slow down or manage hair loss. These may include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride (for men), low-level laser therapy, and hair transplant surgery.
Emotional Impact: -
Hair loss can have psychological and emotional effects on individuals, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Support groups, counseling, and education about available treatments can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of androgenic alopecia.



